Where Do Peanuts Come From?

Where Do Peanuts Come From?
Peanuts, often mistaken as nuts, are actually legumes that belong to the pea family. They have a fascinating history and a global presence, and one particular variety, known as Virginia Peanuts, holds a special place in the culinary world. In this blog post, we will delve into the origins of peanuts, their journey to Virginia, and the unique characteristics of Virginia Peanuts.
The Beginnings: A South American Legacy
Peanuts are believed to have originated in South America, specifically in Brazil or Peru, where indigenous peoples cultivated them for over 2,000 years. These legumes were then transported by Spanish and Portuguese traders to Mexico and eventually found their way to Africa and Europe. However, it wasn't until the early 1700s that peanuts made their way to North America.
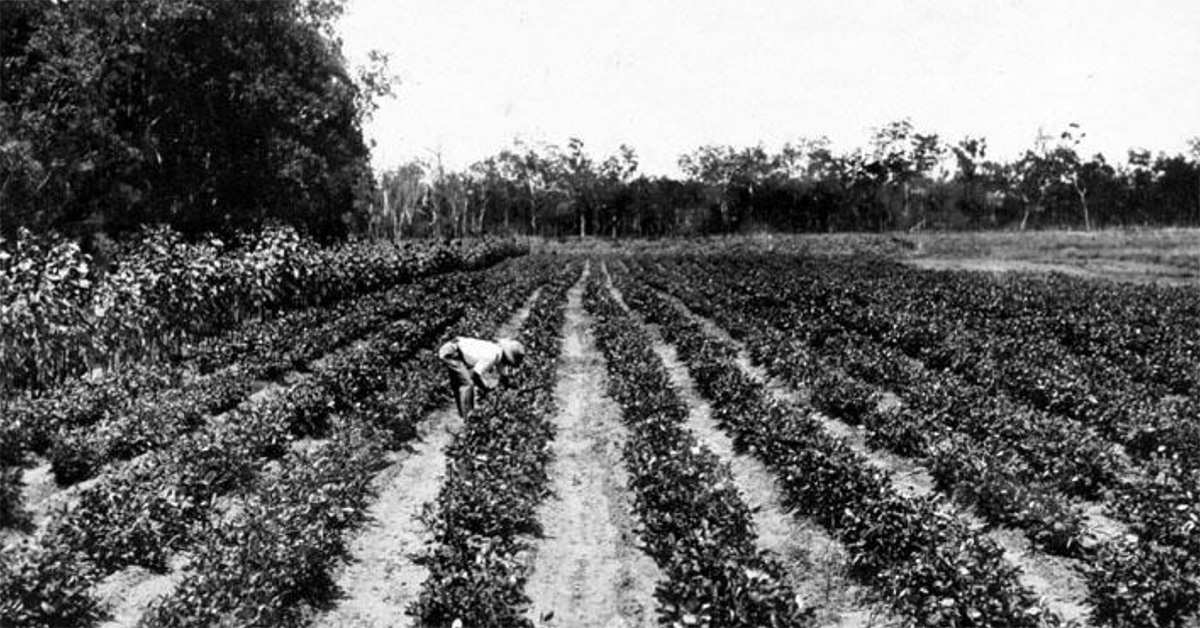
Peanuts Arrive in Virginia
When Africans were forcibly brought to North America as slaves, they carried peanuts with them. Virginia, located in the southeastern region of the United States, became the first known North American location where peanuts were planted. Initially, peanuts were primarily grown for animal feed rather than human consumption. It would take some time before their versatility and delicious flavor would be recognized.
The Rise of Virginia Peanuts
Virginia Peanuts, despite their name, are not exclusive to Virginia. They are one of four distinct peanut varieties, along with Runner Peanuts, Spanish Peanuts, and Valencia Peanuts. While Virginia is a significant producer of this variety, they are also grown in North Carolina, South Carolina, and Texas.
Virginia Peanuts stand out for their size, flavor, and satisfying crunch. They are the largest peanuts among the varieties and have a distinct taste that adds richness to various culinary creations. In fact, Virginia Peanuts are often referred to as the "Ballpark Peanut" because they are the preferred variety sold at baseball games across the country.
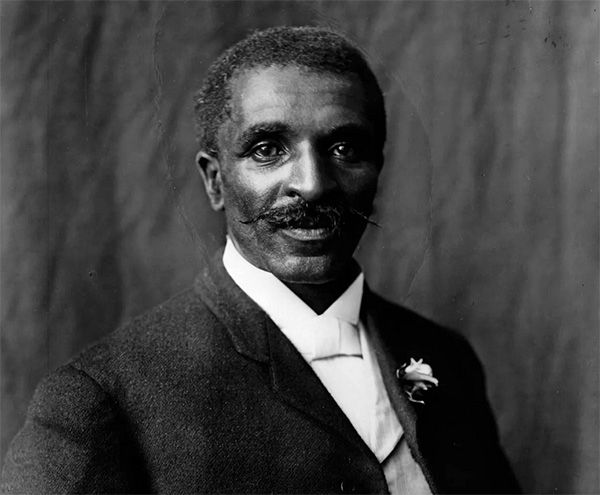
George Washington Carver and the Peanut Revolution
Peanuts gained widespread recognition and popularity in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, thanks in part to the work of George Washington Carver, a renowned biologist. Born into slavery in 1864, Carver would later become a prominent figure in agricultural research and innovation.
Carver recognized the value of peanuts as a cash crop and proposed their cultivation as a rotation crop in the cotton-growing areas of the Southeast, where the destructive boll weevil insect threatened agriculture. Carver's research on peanuts at Tuskegee Institute led to significant advancements in horticulture and the discovery of over 300 uses for peanuts, including peanut butter and various other products.
Virginia Peanuts Today
Today, Virginia Peanuts continue to be a beloved and sought-after variety, offering a combination of size, flavor, and crunch. They are a staple in gourmet snacks and all-natural peanut butter production. Around 15% of the total U.S. peanut production consists of Virginia Peanuts, and they are grown not only in Virginia but also in other states such as North Carolina, South Carolina, and Texas.
Peanuts have become an important crop, contributing over four billion dollars annually to the U.S. economy. They are cultivated in various countries worldwide, including China, Australia, Argentina, and several African nations.
In conclusion, peanuts have a rich history that spans continents and centuries. Virginia Peanuts, one of the four distinct peanut varieties, have left an indelible mark on the culinary world. From their origins in South America to their arrival in Virginia and their rise to popularity, peanuts have become a versatile and beloved legume enjoyed in various forms worldwide.